Will Quantum Computer Interrupt Important infrastructure?

Technology reporter
 Google
GoogleTwenty -five years ago, computer programmers were running to fix the millennium bug amid the apprehension that this would cause banking system crash and aircraft to fall out of the sky.
A lot for everyone’s relief Effect minimum,
Today, some fear is a new significant threat to the world’s digital infrastructure. But this time, we cannot really guess that it will move from theory to reality, while the omnipresent of digital technology means that the problem is even more complicated to fix the problem.
This is because the advent of quantum computing means that it will be difficult to crack into many encryption algorithms that reduce and secure our hyper -connected world.
Quantum computing differs fundamentally for “classical” computing used today. Instead of processing binary bits that exist in one of the two states – one or zero, on or off -quantum uses computing qubeits, which may be present in many states, or superpations.
“It’s so powerful that it is so powerful because you are doing all those potential computations together,” the Director of Research for Computer Science at Surrey University Prof. Nishanth Sestry. This means that it is “very, very efficient, very, much more powerful.”
This means that quantum systems provide the possibility of solving major problems that are beyond classical computers, fields such as medical research and material science, or especially cracked complex mathematical problems.
The problem is some of the same mathematical problems that underline the encryption algorithm that helps ensure confidence, privacy and privacy in today’s computer network.
Today’s computers will take thousands of years to crack current encryption standards like RSA. A appropriately powerful quantum computer, theoretically, can work in minutes.
It is implications for everything from electronic payments and ecommerce to satellite communication. John France, the chief information security officer in the non-profit cyber security organization ISC2, says, “Whatever is weak, it becomes a proper game for those who have access to quantum relevant computers.”
Quantum computers capable of breaking asymmetric encryption are considered years -away.
But progress is being made.
In December, Google said that its new quantum chip is The key includes “successes” and “a useful, large -scale quantum computer route”.
Some estimates say that a quantum device capable of breaking the current encryption will require 10,000 quints, while others say millions will be required. Today’s system has a few hundred.
But businesses and governments still face a problem, as the attackers can cut encrypted information and later decry to it when they achieve access to suitable powerful devices.
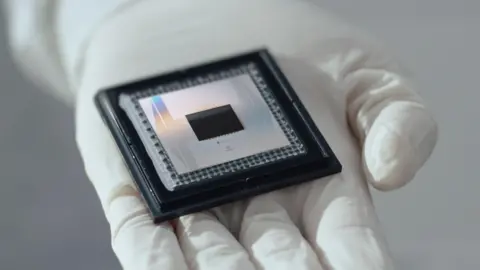 Google
GoogleGreg Wetmore, vice president of the software development at the security firm Entrest, says that if such devices can emerge in the next decade, technology leaders need to ask, “What data is valuable in your organization for that time?”
This can be national security information, personal data, strategic plans and intellectual property and mystery – think about the exact balance of herbs and spices in a soft drink company’s “secret” formula or fast food recipe.
If quantum computing becomes widespread, the danger becomes more immediate with the encryption that protects our daily banking transactions, for example, trivial for potentially rupture.
The good news is that researchers and technology industry are working on the solution to the problem. In August, the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the US released three post quantum encryption standards.
The agency said that these would “from confidential email messages to e-commerce transactions, will secure a wide range of electronic information that pursue the modern economy.” This computer system is encouraging administrators to infection in new standards at the earliest, and another 18 algorithm is being evaluated as backup standards.
 Getty images
Getty imagesThe problem is that this means that a large -scale upgradation process touches almost all our technology infrastructure.
“If you think of the number of things there with asymmetric encryption in them, then these are billions of things. We are really facing the problem of major changes, ”says Mr. France.
It would be relatively easy to upgrade some digital infrastructure. For example, your browser will receive an update from only the seller called Mr. France. “The challenge actually comes in discrete equipment and Internet of Things (IOT),” he continues.
These can be difficult to track down, and geographically inaccessible. Some equipment – heritage equipment in important national infrastructure such as water system, for example – may not be powerful enough to handle the new encryption standards.
Mr. Wetmore says that the industry has managed encryption infections in the past, but “it is a strong dissatisfaction that makes this danger more serious.”
Therefore, it is now trying to help customers to make “crypto agility” using policies installation and automation to identify and manage their cryptographic assets. “It is a mystery to make this transition a systematic and not a chaotic.”
And the challenge extends into space. Pro Stestry states that many satellites – such as Starlink Network – should be relatively straight to upgrade, even if it means to temporarily carry an individual device to offline.
“At any time, especially with Leo (orbit of Earth’s orbit) satellites, you have found 10 to 20 satellites above your head,” Prof. Sashetri. “So, if no one can serve you, then what is okay? There are nine others who can serve you.”
More challenging, they say, “remote sensing” satellites, including people used for geographical or intelligence purposes. They carry a lot of calculation power on the board and usually include some types of safe computing modules. A hardware upgrade means changing the entire device effectively. However, it is now less than a problem for launching more frequent and low -cost satellite, says Pro Sashetri says.
While the effect of the Millennium bug may be minimal in the first days of 2000, this is because the Associate Professor François Dufresir in Cryptography at the University of Bristol says that a lot of work was done to fix it before a known time limit. .
Conversely, he says, it is not possible to guess when the current encryption will weaken.
“With cryptography,” Sri Dupresiroir says, “If someone breaks your system, you will only know that they have got your data.”






